
Tips and Considerations
Universal Steps for Choosing Life and Health




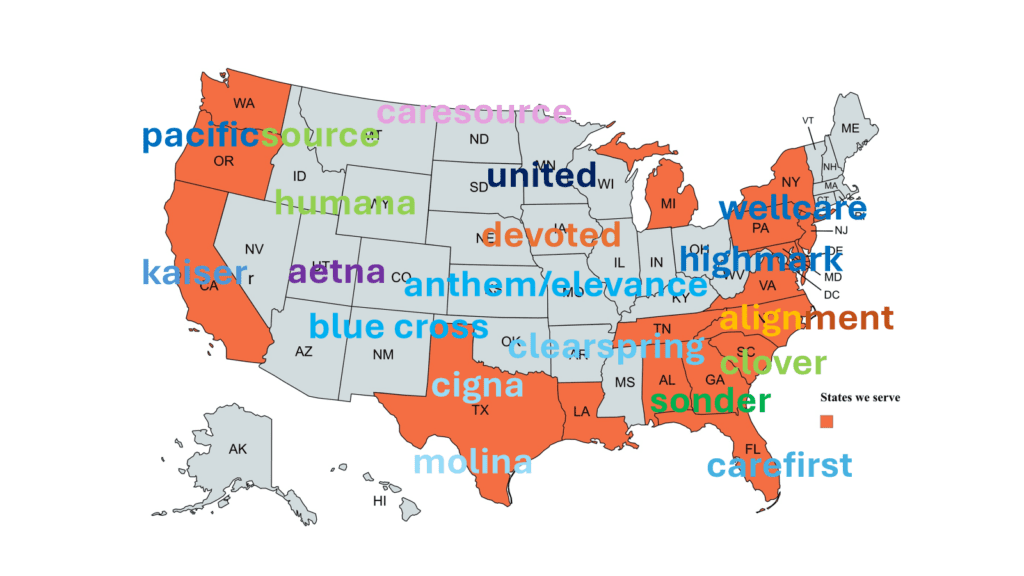
AL NY CA OR DE PA FL SC GA
TN LA TX MD WA MI NC NJ
Offices –
Charlotte, NC- 980-288-5798
Atlanta, GA – 678- 341-0931
Daytona, FL – 386-243- 2927
Knoxville, TN –
Dallas, TX –
Gathersburg, MD –
Portland, OR –
We do not offer every plan available in your area. Currently we represent 12 organizations which offer 51+ products in your area. Please contact Medicare.gov, 1-800-MEDICARE, or your local State Health Insurance Program (SHIP) to get information on all of your options.
Aetna HUMANA Anthem KAISER Alignment MEDICO BCBS NC MOLINA Carefirst PacificSource Cigna PEOPLES HEALTH/UHC Clover SONDER Devoted UHC Highmark WELLCARE/CENTENE